SSH (Secure Shell) provides secure management of network devices. By using SSH, you establish a secure connection to a network device that you access, and your data is sent in encrypted form.
How to Enable SSH in Cisco Router with Packet Tracer

CCNA 2 v7 Lab 1.3.6 Packet Tracer – Configure SSH Instructions Answer key.pdf.pka file download completed 100% scored 2019 2020 2021. Using the command prompt. After you can see the command prompt below you will get your Ip address. Ping – Check packets. Running this command sends test packets over the network to the target system. System Information. Systeminfo get all the information about your pc / laptop in details Network Statistics. Router host name is the name which you will see in the command line interface for all of your routers in a network, while Router Display name is used for visually identifications of your routers. Step 4: For CCNA using command line interface is recommended, click on the CLI tab for opening command line interface. The tracert command is a Command Prompt command that's used to show several details about the path that a packet takes from the computer or device you're on to whatever destination you specify. You might also sometimes see the tracert command referred to as the trace route command or traceroute command.
SSH is a much safer protocol than the Telnet protocol and uses the TCP 22 port by default. The port number may vary.
Packet Tracer Commands List
There are 2 versions of the SSH protocol. These; Version 1 and Version 2.
Packet Tracer Command Line
SSH V1 exploits several patented encryption algorithms and is vulnerable to a well-known vulnerability that could allow an attacker to enter data into the communication flow.
SSH V2, this release has an advanced key exchange algorithm that is not vulnerable to the same abuse and includes more powerful and comprehensive features:
• Encryption such as 3DES and AES.
• Use voice encryption Message Verification Code (MAC) algorithms for integrity checking.
• Support for public-key certificates.
We recommend that you use SSH V2 as far as possible to remotely manage network devices.
To enable SSH in the real scenario, make sure that the file name of your Cisco IOS software is k9 (crypto).
Step 1
First, run Packet Tracer and then create a network topology as shown in the image below. Add an additional Router to the workspace, because after configuration we will connect the Router to the Router with SSH.
Step 2
Open the CLI prompt by clicking on the SYSNETTECH Router and press Enter to skip the initial configuration.
Step 3
To enable SSH on the router, perform the following commands in order.
Step 4
Configure the IP settings of PC1 as follows.
Step 5
To quickly configure the R1’s interface, double-click on it, click the Config tab in the window that opens, and then configure the Port Status option of the GigabitEthernet0/0 interface to On, then assign the IP address.
Step 6
To test whether SSH is running, open the PC1 prompt and establish a connection using the command below.
All Packet Tracer Commands
Step 7
Enter the user name and password you created, and as soon as you press Enter, the connection will be established as in the image below.
Step 8
After executing the show ssh command on PC1 Command Prompt, you can check the version of the SSH protocol that is linked.
Step 9
In this step, execute the following command to make SSH from router to router.

Step 10
In the same way, enter the user account information you created on the Cisco Router and press Enter.
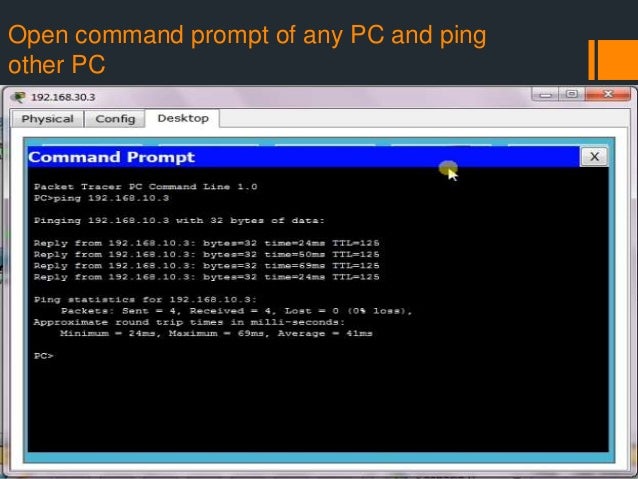
Step 11
As you can see in the image below, a successful SSH connection is made.
Show Commands
Video
With the simulator, you can watch the video below to enable SSH on the router and connect from the PC and also subscribe to our YouTube channel to support us!
Final Word
In this article, after examining how to enable SSH, we have connected with SSH from PC to Router and Router to Router to verify the connection. In the real scenario, to configure SSH on Routers, make sure the IOS image has k9 (crypto). Thanks for following us!
Related Articles
♦ Packet Tracer VLAN
♦ Packet Tracer Inter-VLAN
♦ Packet Tracer Static NAT
♦ Packet Tracer Dynamic NAT
♦ Packet Tracer PAT
9.2.3.3 Packet Tracer – Using the Ping Command Answers
Packet Tracer – Using the Ping Command (Answers Version)
Answers Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the Answers copy only.
Topology
Objectives
Use the ping command to identify an incorrect configuration on a PC.
Background / Scenario
A small business owner learns that some users are unable to access a website. All PCs are configured with static IP addressing. Use the ping command to identify the issue.
Step 1: Verify connectivity.
Access the Desktop tab > Web Browser of each PC and enter the URL www.cisco.pka. Identify any PCs that are not connecting to the web server.
Note: All of the devices require time to complete the boot process. Please allow up to one minute before receiving a web response.
Which PCs are unable to connect to the web server?_____________ PC2
Step 2: Ping the web server from PC2.
- On PC2, access the Command Prompt from the Desktop tab.
- Type ping www.cisco.pka.
Did the ping return a reply? What is the IP address displayed in the reply, if any?____________________________________________________________________________________
There was no reply. No IP address was displayed in the message.
Step 3: Ping the web server from PC1.
- On PC1, access the Command Prompt from the Desktop tab.
- Type ping www.cisco.pka.
- Did the ping return a reply? What is the IP address returned, if any?____________________________________________________________________________________
Reply was returned with 192.15.2.10 as the IP address for www.cisco.pka.
Step 4: Ping the IP address of the web server from PC2.
- On PC2, access the Command Prompt from the Desktop tab.
- Attempt to reach the IP address of the web server with the command ping 192.15.2.10.
- Did the ping return a reply? If so, then PC2 is able to reach the web server via IP address, but not domain name. This could indicate a problem with the DNS server configuration on PC2.
Step 5: Compare the DNS server information on PC2 with other PCs on the local network.
- Access the Command Prompt of PC1.
- Using the command ipconfig /all, examine the DNS server configuration on PC1.
- Access the Command Prompt of PC2.
- Using the command ipconfig /all, examine the DNS server configuration on PC2. Do the two configurations match?
Step 6: Make any necessary configuration changes on PC2.
- Navigate to the Desktop tab of PC2, make any necessary configuration changes in IP Configuration.
- Using the Web Browser within the Desktop tab, connect to www.cisco.pka to verify that the configuration changes resolved the problem.
- Click the Check Results button at the bottom of this instruction window to check your work.